February 09, 2026
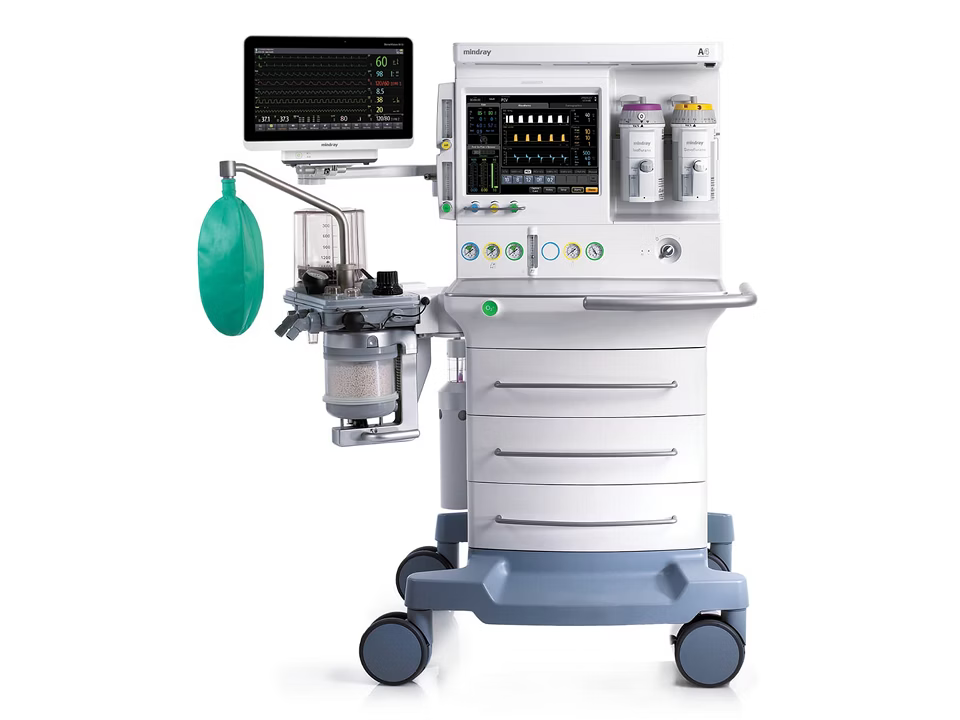
Anesthesia machine is a crucial part of operative treatment and enables people to receive safe and effective anesthesia while surgery. It is designed to provide consistent concentrations of medical gases and volatile anaesthetic vapour, while also allowing for assistance with patient breathing and oxygenating patients who are undergoing surgery. Accuracy and dependability of the anaesthesia machine are primary concerns that bother Anesthesiologist during the surgery.
Malfunctioning or improperly calibrated anaesthetic equipment or machinery may lead to serious, life-threatening adverse effects such as hypoxic state due to lack of, or improper concentration of oxygen in the environment; hypercapnia, i.e., excess carbon dioxide; overdose of anaesthetic; and anaesthetic-related incidents of hazards involving equipment. Therefore, strict and consistent adherence to established safety protocols is of utmost importance for reducing potential risks, ensuring the optimal functionality of the anaesthesia machine, and preserving the quality of patient outcomes. This blog examines the fundamental safety protocols associated with anesthesia and the practices one must undertake to contribute to health safety.
What is an Anesthesia Machine?
Multiple hospitals utilise anesthesia machines as one of their primary components for patient care in the operating area. This device allows for the administration of gaseous substances to patients while also allowing for the constant administration of anesthetics during surgical procedure. The main function of an anesthesia machine is to allow the anesthesiologist to provide support for the oxygenation of the patient and to provide support for the ventilation of the patient. It also provides the means for the anesthesiologist to keep track of the patient’s respiratory status.
Each machine has a breathing system designed to deliver the needed gases to the patient and to eliminate exhaled carbon dioxide from the patient after the patient has completed the procedure. Moreover, many newer anesthesia machines come equipped with integrated ventilators, monitoring systems, and additional safety devices to ensure proper gas delivery and patients’ safety. They have various safety features built into them to help prevent the creation of hypoxic mixtures and any equipment-related problems.
Intraoperative Safety Protocols for Anesthesia Machines
Consistent monitoring of the patient and compliance with safety standards throughout the administration of anesthesia are critical for minimising the incidence of anesthesia-related complications. To achieve this, the anesthesia apparatus and delivery system must remain operational at all times during this period while anesthetics are delivered. Additionally, intraoperative safety standards will assist in maintaining the delivery of oxygen, the adequacy of mechanical ventilation, and providing early notification of equipment-related problems. More such safety protocols to be followed in a comprehensive manner to ascertain the well-being of patients during the treatment are mentioned below.
1.Continuous Oxygen Monitoring: One of the most important safety precautions when administering anesthesia is continuous oxygen monitoring. An oxygen analyser should continuously measure the inspired oxygen concentration to ensure an adequate supply of oxygen and prevent the delivery of hypoxic gas mixtures. Audible and visual alarms should be provided to alert the anesthesiologist when the inspired oxygen concentration falls below acceptable levels. In addition, the anesthesiologist should confirm the delivery of oxygen throughout the length of a procedure, as well as after any changes made to gas flow settings or the anesthetic concentration, to ensure that adequate oxygen is provided at all times.
2.Ventilation Safety: An important aspect of maintaining ventilation safety is the assurance that gases can be effectively exchanged during the period of anesthesia due to the proper functioning of the anesthesia ventilator. Tidal volume and respiratory rates delivered to the patient by the anesthesia ventilator should be observed to ensure they are correct. The monitoring of airway pressure will assist in identifying problems early, such as obstructed airways, circuit disconnections and/or excessive airway pressures. Moreover, alarms for high and low airway pressures need to be maintained in active mode in order to quickly notify the Anesthesiologist if the patient is deviating from a normal set of ventilation parameters.
3.Pressure Relief and Scavenging Systems: The adjustable pressure-limiting (APL) valve or pressure relief valve also assists in preventing excessive airway pressures, reducing the likelihood of barotrauma occurring to the patient while providing adequate mechanical ventilation and preventing excessive inhalation of waste anesthetic gas. The scavenging system must also be checked regularly to ensure that excess anesthetic gas is effectively removed from the circuit.
4.Alarm Systems: Alarm systems are integrated into the anesthesia machine to be utilised as a warning system for providers during the provision of anesthesia delivery to a patient. The alarm should always be activated and audible for low oxygen supply pressure, circuit disconnect, high airway pressure, and power failure. Silence of any alarm systems must not occur until the problems identified have been resolved. Moreover, if the alarm system is muted, the potential for life-threatening conditions and a malfunction of the equipment may exist.
5.Color coding of the Gas cylinders, PISS (Pin Index Safety System) & DISS (Diameter index Safety System) prevent wrong connections.
Conclusion: Grow in the Field of Anesthesia Technology with DPMI
Anesthesia machine safety protocols play an essential role in protecting patients and facilitating the safe and effective performance of surgery. Anesthesia-related complication prevention relies on the implementation of each of these safety protocols as well as the ongoing monitoring, appropriate alarm management and the post-use servicing and maintenance of anesthesia machines. The continued implementation of these protocols also depends on the skill of the professionals who utilise them and maintain close observation of all machine functions to ensure that quality anesthesia is delivered and that all patients achieve optimal results from their procedures.
For the young generation that is aspiring to build a career in the budding field of anesthesia technology, a strong foundation in equipment safety and clinical protocols is essential. Enrolling in a professionally designed operation theatre course at DPMI provides comprehensive theoretical knowledge along with hands-on clinical training. With experienced faculty, modern laboratories, and industry-oriented curriculum, DPMI prepares students to meet real-world operating theatre challenges confidently and competently.