November 12, 2025
In recent years, the widespread interest in prebiotics and probiotics in clinical research and nutritional science has picked up pace, largely due to their crucial role in maintaining gut health, immunity, and overall wellbeing. While they are most commonly recognized for their digestive benefits, prebiotics and probiotics also play a key role in immunity responses, metabolism, and mental health. Comprehensive scientific research has established a link between gut microbiota balance and enhanced physical and mental health, as well as a reduced risk of disease. This has underscored the significance of prebiotics and probiotics in dietary and therapeutic strategies for health and wellness improvement. When used together, they create a synergistic relationship that promotes optimal gut function and systemic health.
What Are Probiotics?
Probiotics are living microorganisms that provide measurable health benefits to the host when consumed in adequate amounts. They are most commonly bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species, though certain yeasts like Saccharomyces boulardii also function as probiotics.
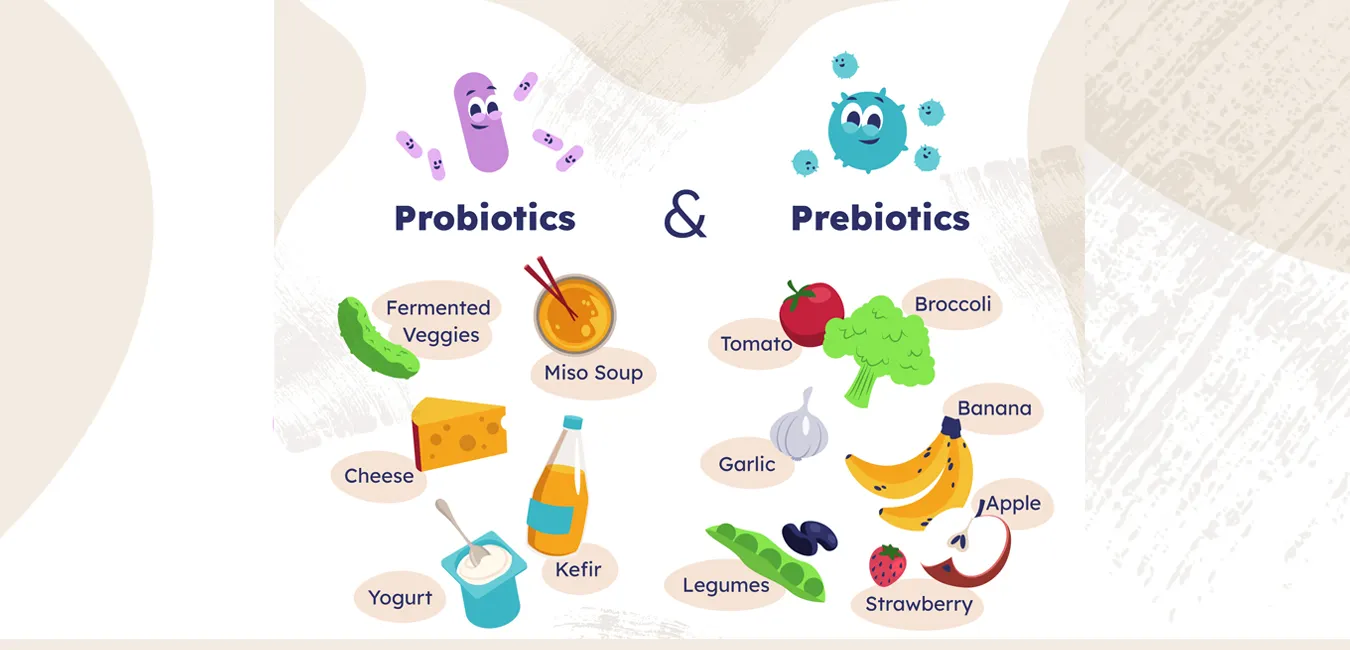
Probiotics help maintain gut microbial balance by inhibiting pathogenic organisms, supporting digestion, and promoting immune function. In addition to gut health, new data shows that probiotics can potentially regulate metabolism, suppress inflammation, and play a role in the gut-brain axis, which can also affect mental health. Probiotics occur naturally in fermented foods, like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut, as well as dietary supplements formulated for specific therapeutic outcomes.
Table.1 Common Probiotics and their Benefits
| Probiotic | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Lactobacillus Acidophilus | Aids in relieving symptoms of lactose intolerance and promotes digestive balance. |
| Lactobacillus Rhamnosus GG | Reduces risk of gastrointestinal infections and supports children’s gut health. |
| Bifidobacterium Bifidum | Enhances nutrient absorption and supports a healthy intestinal environment. |
| Saccharomyces Boulardii | Helps prevent and manage antibiotic-associated diarrhea and restores gut flora balance. |
What are Prebiotics?
Prebiotics are non-digestible dietary fibers and compounds that nourish beneficial microorganisms in the gut, particularly probiotics. They act as substrates that selectively stimulate the growth and activity of health-promoting bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract. Prebiotics create an environment where probiotics can flourish, and are therefore critical to maintaining microbial balance and long-term gut health.
Prebiotic compounds are naturally found in many plant-based foods such as onions, garlic, bananas, leeks, chicory root, and whole grains, and frequent consumption of prebiotics promotes not only digestive health but also immunity, metabolic regulation, and mineral absorption. Recent research also suggests that prebiotics can positively influence mental health, by affecting the gut-brain axis.
Table.2 Common Prebiotics and Their Benefits
| Prebiotic | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Pectin | Regulates cholesterol levels and supports heart health. |
| Galactooligosaccharides (GOS) | Aid in reducing symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). |
| Fructooligosaccharides | Helpful in improving bone health and calcium absorption. |
| Inulin | Encourages the feeling of satiety by promoting the release of hormones that regulate appetite, which leads to a decrease in total calorie intake. |
The Prebiotic–Probiotic Synergy: Need for Both
Maintaining gut health by focusing on either prebiotics or probiotics alone is laborious for the human body. The interaction between both the fibers and microorganisms creates an internal environment that not only introduces beneficial bacteria but also supports them to function properly. This mutual relationship enables lasting benefits for digestive and systemic health. Apart from the well-established uses of prebiotics and probiotics, other benefits of the same are highlighted below.
- Enhanced Efficacy: Over the past few years, research has shown that the co-administration of prebiotics and probiotics, also called synbiotic, leads to better clinical treatment outcomes than either component alone. This synergistic effect has been demonstrated in the management of gastrointestinal conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), antibiotic-associated diarrhea, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Mutual Dependence: Prebiotics serve as fermentable substrates for probiotics, allowing them to produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), like butyrate and acetate, which help colon health, have anti-inflammatory effects, and strengthen intestinal barrier integrity.
- Modulation of Metabolic Health: The combined effects of prebiotics and probiotics have been linked to better metabolic regulation, including improved insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism. Synbiotics improve glucose homeostasis and potentially offer cardioprotective effects while reinforcing their role beyond gastrointestinal health.
Conclusion: The Lasting Impact of Probiotics and Prebiotics
Utilizing prebiotics and probiotics maximizes the ability to support gut health while improving general health. The probiotic adds beneficial microbes to your gut, while prebiotics are the food that allows these microbes to thrive. When combined, they promote not only digestive efficiency but also contribute to aspects of immune modulation, metabolic regulation, and even potentially aspects of mental health. A diet rich in fiber, fermented foods, and clinically validated synbiotic supplements fosters a robust and diverse gut microbiome. This not only improves digestive health but also represents an important step towards achieving long-term systemic wellness.
Also Read: The Invisible Helpers: How Probiotics and Gut Microbes Shape Our Health