November 21, 2025
In the healthcare environment maintaining sterility is a fundamental aspect of infection control and patient safety. Sterilization effectively eliminates all forms of microorganisms but it is the process of packaging sterile articles that ensures sterility is preserved until the point of use. Integrity of the packaging directly influences the success of sterilization, as improper packing can lead to contamination during handling, storage or transportation.
Therefore, understanding the principles, materials and techniques involved in packing the sterile articles is crucial for healthcare professionals, who are engaged in surgical, diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Proper packing not only maintains asepsis but also contributes to operational efficiency, safety and adherence to hospital infection control standards.
Why is the Packing of Sterile Articles Done?
The packing of sterile items is a part of infection control procedure that ensures sterilized items stay uncontaminated before being used. Packing serves as a barrier to protect the sterilized items from contaminating the environment, such as dust, microorganisms, moisture, etc., which would break the aseptic state. Primary objectives of packing the sterile articles are mentioned below:
- To allow penetration of sterilizing agents: Allows the sterilizing medium to adequately access all surfaces through the process.
- To provide physical protection: Protects delicate instruments from damage during handling and transport.
- To ensure easy identification and organization: Labels and standardized packaging techniques assist in rapid identification and workflow efficiency.
- To extend the shelf life of sterile items: Allows materials to remain sterile and ready for usage for a longer period of time when stored appropriately.
- To promote aseptic handling: Enabling health care professionals to open packages safely while maintaining sterility.
Packaging of Sterile Articles
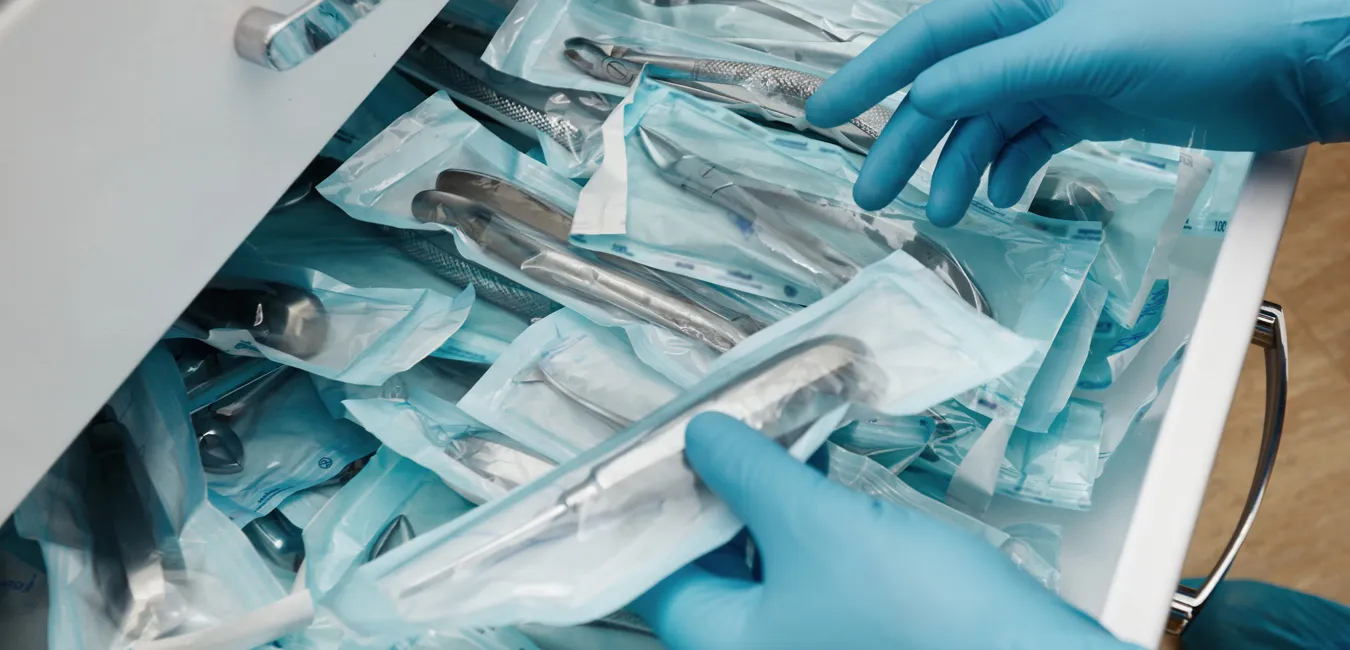
Packing sterile items starts with a well-planned process that depends on sufficient knowledge of specific materials in order to accomplish effective sterilization and maintain sterility for the right amount of time. The choice of packing material and packing method can directly affect the effectiveness of sterilization and the safety of sterilized items, and all materials should be ideally designed specifically for sterilization methods.
1. Selection of Suitable Packing Materials
The material chosen to pack the sterile articles must allow the sterilizing agent, i.e., steam, gas, or dry heat, to penetrate while preventing recontamination of the items within the material after sterilization. Commonly used materials are mentioned below:
- Muslin: This cloth is reusable and extremely permeable. It is highly preferred for steam sterilization in autoclaves.
- Kraft paper: It is a single-use paper that provides a highly efficient microbial barrier. It is considered the best to use when dry heat or gas methods are applied for packaging.
- Plastic Pouches: These are mainly used for smaller or delicate instruments. Moreover, these allow you to see what is in the pouch and provide a non-touch aseptic opening.
2. Packaging Procedure
Once the appropriate materials have been selected, packing should be done with extreme care and aseptic technique in order to ensure that there is no contamination. The process involves several important stages that will preserve the sterility of the item until the time it is used.
The process begins with inspection and cleaning, during which all instruments should be scrutinized, cleaned, dried, and evaluated for workability and damage. The next stage is systematic arrangement, when all instruments should be grouped together logically, either by type or as part of a surgical set. Moreover, all sharp or fragile instruments should be properly secured in order to prevent breakage.
Next process is wrapping, when the selected material should be folded firmly around the items, however, still leaving space for sterilizing agents to penetrate. Proper sealing should then be done using autoclave tape, heat seals, or clips, keeping in mind to properly close the package without compromising sterility. As a final step, all packs must be labeled with important information regarding contents, the date of sterilization method used, initials of the packaging person.
3. Storage and Handling of Sterile Packs
After sterilization, the packs need to be cooled and stored in a clean, dry, dust-free storage area. They should have minimal handling and any pack that is torn, wet, or unsealed should be treated as non-sterile and re-packed for re-sterilization.
Conclusion
Sterile OT instruments are packed using materials like medical-grade paper, non-woven wrap, SMS (Spunbond-Meltblown-Spunbond) fabric, crepe paper, Tyvek, and sterilization pouches. These materials allow proper steam or gas penetration, maintaining sterility, resist tearing, and ensure safe handling and storage of surgical instruments until use.Proper packing maintains the sterilized items’ efficiency and contributes to the overall quality of patient care and clinical efficiency.
Also Read: Immunoelectrophoresis: Principle, Techniques and Applications