October 17, 2025
Introduction
Immunoelectrophoresis (IEP) is a powerful technique that combines electrophoresis and immunodiffusion to analyze proteins, particularly immunoglobulins in biological samples. It is widely used in clinical diagnostics and research to detect and quantify specific proteins. It also helps to study antigen-antibody interactions and identify protein abnormalities in diseases such as multiple myeloma and immune deficiencies.
Principles of Immunoelectrophoresis
Immunoelectrophoresis is based on two key principles:
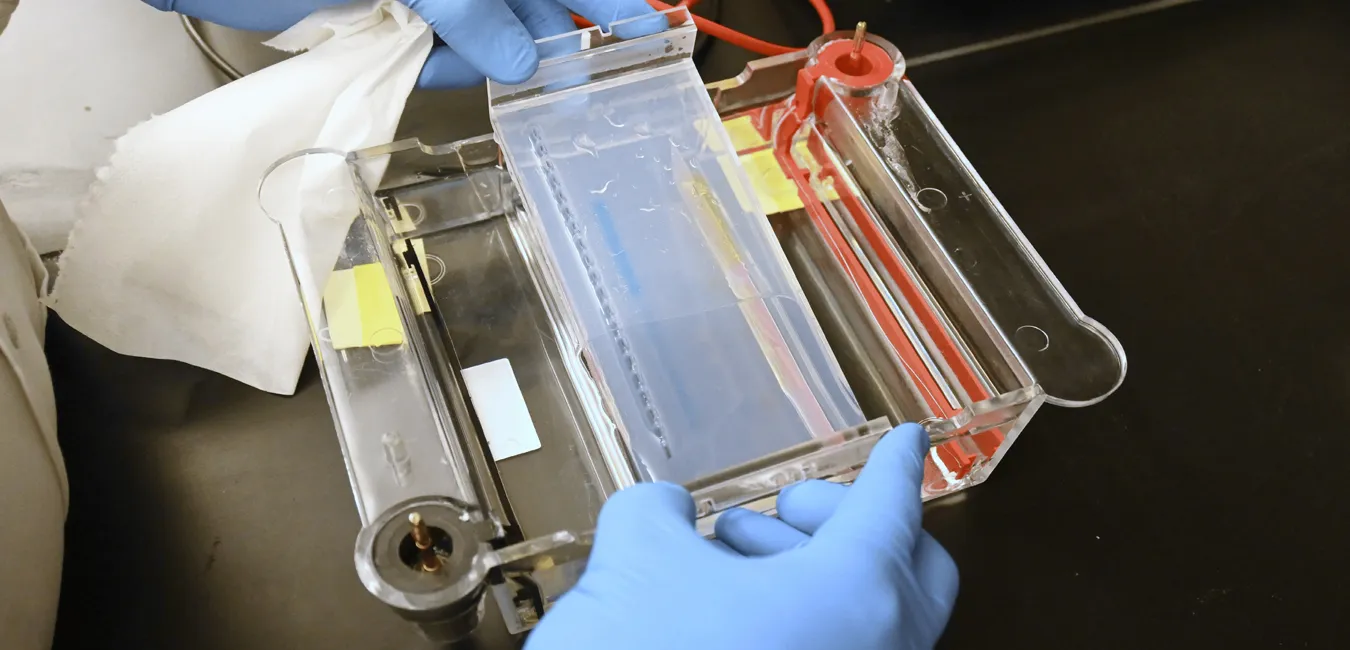
Electrophoresis: Proteins in a sample are separated according to their charge and size by applying an electric field on an Agarose gel or another suitable medium.
Immunodiffusion: After electrophoresis, specific antibodies are applied to the gel, and antigen-antibody interactions lead to the formation of visible precipitation arcs, indicating the presence and quantity of specific proteins.
The technique is highly specific because it relies on the selective binding of antigens and antibodies, making it useful for detecting abnormalities in protein composition.
Techniques of Immunoelectrophoresis
There are different approaches for performing immunoelectrophoresis, each with its own advantages and specific applications:
1. Classical Immunoelectrophoresis (IEP)
It involves two steps: electrophoretic separation of proteins and immunodiffusion.
The sample is applied to a gel and subjected to electrophoresis, leading to the separation of proteins.
A trough is cut parallel to the migration path and specific antibodies are added.
As the antigens and antibodies diffuse, they form precipitation arcs at optimal concentrations.
2. Crossed Immunoelectrophoresis (CIE)
A two-dimensional approach that enhances resolution.
In the first step, proteins are separated by electrophoresis.
In the second step, the separated proteins are electrophoresed perpendicularly into an antibody-containing gel.
This provides a quantitative assessment of protein components.
3. Rocket Immunoelectrophoresis (Laurell’s Rocket Electrophoresis)
A rapid technique for quantifying proteins in a sample.
The antigen is mixed with agarose containing a specific antibody.
Upon electrophoresis, antigen-antibody complexes form precipitin peaks resembling rockets.
The height of the rocket correlates with the antigen concentration.
4. Counter Immunoelectrophoresis (CIEP)
A rapid technique where antigens and antibodies migrate towards each other under an electric field. This is used for detecting microbial antigens in clinical samples.
Applications of Immunoelectrophoresis
Immunoelectrophoresis has several important applications in clinical and research settings:
1. Clinical Diagnostics
Detection of Immunoglobulin Abnormalities: Helps to identify diseases like Multiple myeloma, Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia and immunodeficiency disorders by analyzing immunoglobulin levels.
Diagnosis of Paraproteinemias: Identifies monoclonal gammopathies and other plasma cell disorders.
Detection of Complement Deficiencies: Used to analyze complement proteins in immune system disorders.
Autoimmune Disease Diagnosis: Identifies specific autoantibodies in diseases like Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) and Rheumatoid Arthritis.
2. Research Applications
• Protein Characterization: Helps in studying the structural and functional properties of proteins.
• Antibody Profiling: Used to evaluate antigen-antibody interactions in immunological research.
• Biopharmaceutical Development: Quality control in the production of therapeutic antibodies and vaccines.
3. Microbial Antigen Detection
Detects bacterial and viral antigens in infections such as meningitis and pneumonia. It is used in rapid diagnostic tests for infectious diseases.
Conclusion
Immunoelectrophoresis is a crucial technique in clinical diagnostics and immunological research, allowing the identification and quantification of proteins with high specificity. Variants like crossed immunoelectrophoresis and rocket electrophoresis have further enhanced its applications, making it a valuable tool in the study of immune responses, disease diagnostics and protein characterization.
While newer techniques like Western blotting and mass spectrometry offer greater sensitivity, immunoelectrophoresis remains an essential, cost-effective and widely used method in immunology and biochemistry laboratories.
By: Ms. Shivani Sinha
Faculty of Biochemistry
Also Read: Vacutainer Blood Collection Tubes